Physical cybersecurity in data centers is a critical aspect of overall cybersecurity. It focuses on protecting the physical infrastructure, assets, and personnel within a data center facility to prevent unauthorized access, theft, damage, or disruption to the data center operations.
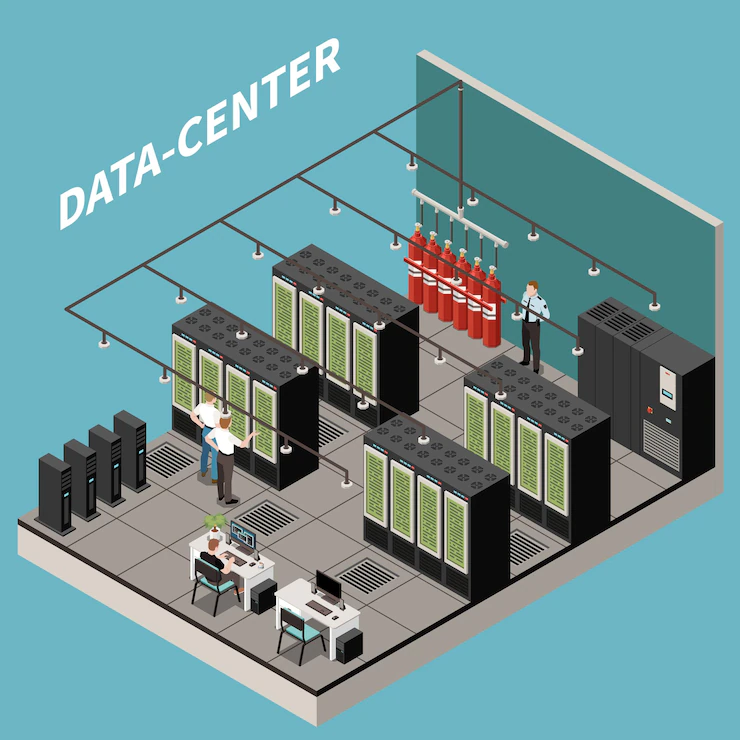
Imagen de macrovector en Freepik
INTRODUCTION
Here are some key considerations and measures taken to ensure physical security in data centers:
Access Control: Data centers employ strict access control measures to limit entry to authorized personnel only. This includes the use of physical barriers such as gates, fences, and perimeter security, as well as secure entry points with access cards, biometric systems, or key codes.
Video Surveillance: Data centers are equipped with comprehensive video surveillance systems to monitor and record activities within the facility. Cameras are strategically placed to cover entry points, server rooms, and other critical areas. The recorded footage can be used for investigation and monitoring purposes.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): IDS systems are deployed to detect unauthorized entry or suspicious activities. These systems use sensors, motion detectors, and other technologies to identify potential security breaches and trigger alerts or alarms for immediate response.
Security Guards: Trained security personnel are often present on-site to monitor and respond to security incidents. They play a vital role in patrolling the facility, verifying visitor access, and providing immediate assistance during emergencies.
Environmental Controls: Data centers maintain proper environmental controls to ensure the optimal operating conditions for servers and other equipment. This includes measures such as temperature regulation, humidity control, fire suppression systems, and water leak detection systems to prevent physical damage and minimize downtime.
Asset Management: Data centers implement asset management procedures to track and monitor the movement of equipment, servers, and other physical assets within the facility. This helps prevent theft, loss, or unauthorized removal of critical hardware.
Secure Rack Cabinets: Server racks and cabinets are secured with locks to restrict physical access to the servers. Only authorized personnel should have access to the server hardware.
Redundancy and Disaster Recovery: Data centers often incorporate redundancy and disaster recovery measures to ensure uninterrupted operations. This may include backup power supplies, redundant network connections, and off-site data backups.
Employee Training: Data center staff receive regular training on physical security protocols, including identifying and reporting suspicious activities, handling emergencies, and adhering to access control procedures.
Overall, physical security measures in data centers work in conjunction with technical cybersecurity measures to create a layered defense approach. By protecting the physical infrastructure and assets, data centers can mitigate the risk of unauthorized access, theft, and physical damage to critical systems and data.

Image by rawpixel.com on Freepik
NEW LAYERED PROTECTION STRATEGIES
Let’s see how layered protection strategies are currently being established and what they are. Nowadays, with the growing number of data centers around the world, the information stored in them is becoming increasingly sensitive. A service interruption can cause significant damage to both the company that owns them and the users whose operations or activities depend on their proper functioning.
For this reason, it is essential to implement multiple physical security measures to prevent unauthorized access, theft, damage or interruption of operations in the data center.
IMPLICATIONS
Physical security in a data center refers to the measures and protocols implemented to protect the physical infrastructure, assets and confidential information stored in the facility.
In an ever-growing market, the goal is to implement various security measures to reduce the risk of unauthorized users accessing data and other resources in the data processing center (DPC).
Layered security systems: a growing trend
The layered approach to physical security in the data center is becoming a growing trend. Each layer has a set of protective measures tailored to its specific characteristics.
Thus, the first layer is the perimeter of the data center. The second layer deals with the protection of the facilities. The third layer protects IT equipment, and the fourth layer focuses on security at the rack level.
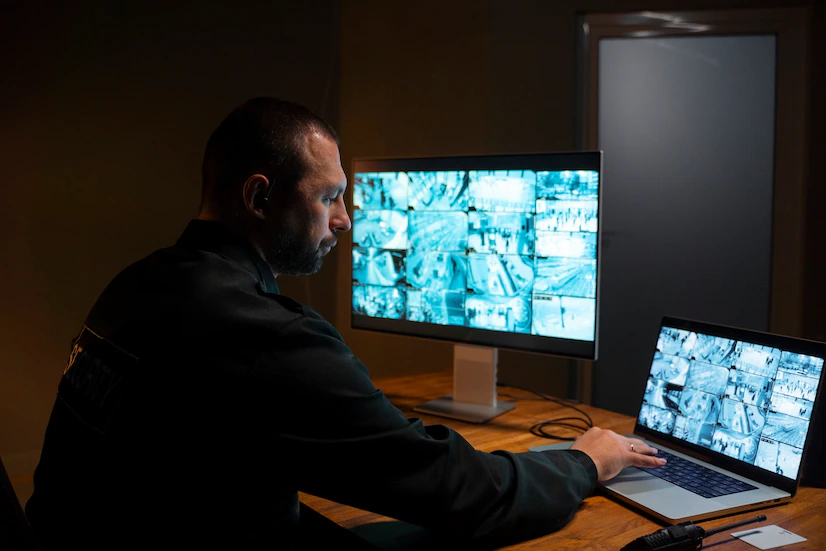

Imagen de pikisuperstar en Freepik
PERIMETER SECURITY
At the data center perimeter level, various systems must be implemented to ensure physical security. However, some installations will require more restrictive measures than others. Sectors such as banking and companies that provide services to third parties often place special emphasis on physical security.

Imagen de macrovector en Freepik
Some of these measures include 24-hour video surveillance services, fences or walls around the perimeter, exterior lighting, well-defined access control points, access security systems (access cards, biometric control or other similar systems), physical surveillance personnel, and technical personnel available around the clock.
INSTALLATION SECURITY
In this layer, systems are installed to reinforce security in the event of a perimeter access violation. An example of this are IDS (Intrusion Detection System) systems, which alert security personnel to any unauthorized access. These systems can include motion sensors, door sensors and other technologies to monitor physical access.

Imagen de Freepik
Other examples are alarm systems, which can be triggered by audible alerts, notifications to security personnel or automatic responses. Mantraps, which are rooms with multiple doors that require authentication (or double authentication), are also used to prevent unauthorized persons from gaining access to the facility through social engineering or tracking of authorized persons.
At this point, it is also important to highlight fire protection systems in data centers.
EQUIPMENT SECURITY
The goal in this layer is to restrict access to computer rooms as much as possible using various verification methods. This includes classic passwords, access cards, electronic keys or biometric authentication methods.
Another important aspect of physical security at the equipment level is environmental control. This involves ensuring that DPC equipment for temperature and humidity control is present in this layer of protection, ensuring optimal hardware operation.
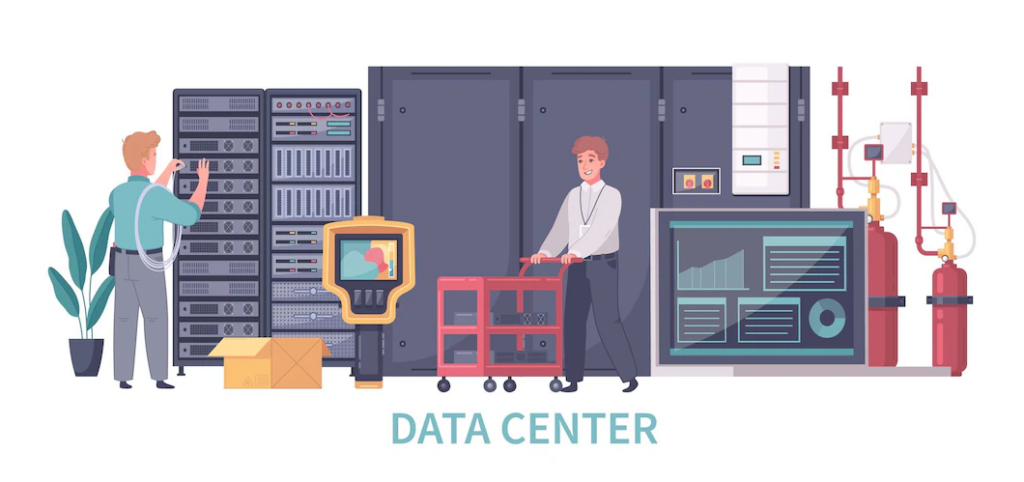
Imagen de macrovector en Freepik
In addition, this point highlights the importance of asset tracking and logging, with the aim of monitoring any movement of equipment within the facility. This allows preventing hardware theft and sharing information within the equipment about any change in the location of the equipment.
RACK-LEVEL SECURITY
This layer is critical to minimize internal threats. Here, staff awareness and training are of great importance, as they help to prevent possible bad practices (intentional or not) related to racks.

Imagen de vectorpocket en Freepik
Some common security systems in this layer are electronic locking of server racks, video surveillance of racks, biometric systems to control access, as well as metal detection.
CONCLUSIONS
Physical security in data centers is crucial to protect confidential information and prevent service interruptions. The implementation of layered strategies offers greater protection by addressing different aspects of security at each level. From the data center perimeter to the protection of equipment and racks, measures such as surveillance, access control and intrusion detection are applied. These measures ensure a secure environment for the operation and safeguarding of data in data centers.

Imagen de creativeart en Freepik
Some of our contents have been created by ChatGPT, a large language model trained by OpenAI, based on the GPT-3.5 architecture, with the knowledge cutoff date of 2021
